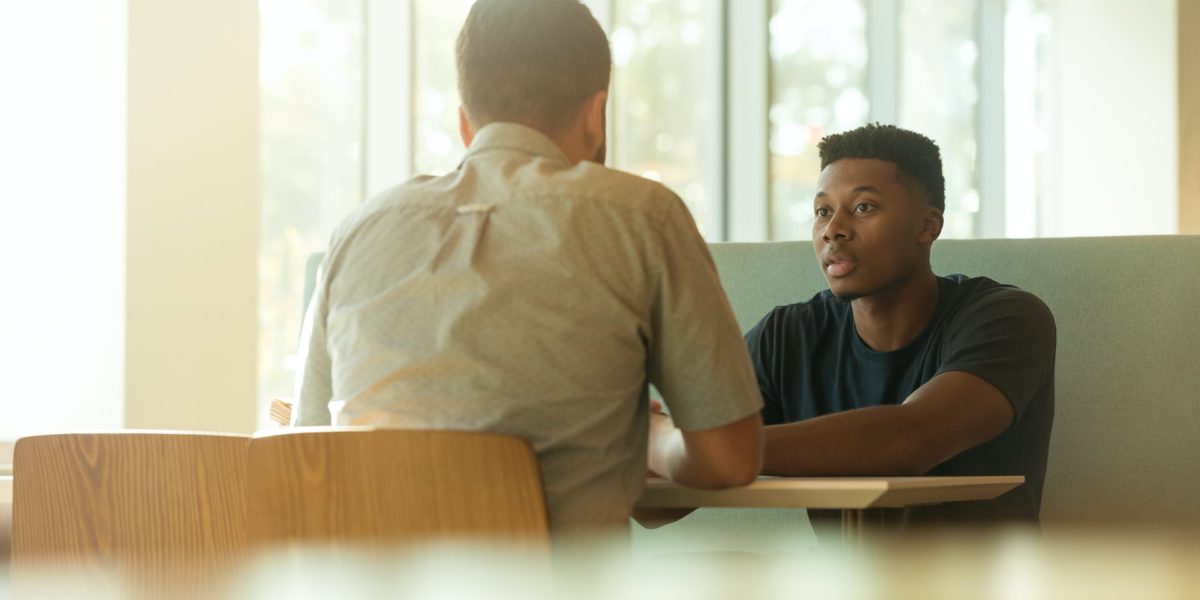
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) refers to any means of settling disputes outside of the courtroom. ADR typically includes negotiation, arbitration, mediation and conciliation. Public courts may be asked to review the validity of ADR methods, but they will rarely overturn ADR decisions and awards if the disputing parties formed a valid contract to abide by them. Arbitration and mediation are the two major forms of ADR. While the two most common forms of ADR are arbitration and mediation, negotiation is almost always attempted first to resolve a dispute. It is the foremost mode of dispute resolution. Negotiation allows the parties to meet in order to settle a dispute. The main advantage of this form of dispute settlement is that it allows the parties themselves to control the process and the solution.
The rising popularity of ADR can be explained by the increasing caseload of traditional courts, the perception that ADR imposes fewer costs than litigation, a preference for confidentiality, and the desire of some parties to have greater control over the selection of an individual or individuals who will decide their dispute. Some of the senior judiciary in certain jurisdictions in Pakistan is strongly in favor of this ADR by using mediation for settlement of disputes.